The Ultimate Guide to Growing and Caring for Russian Sage
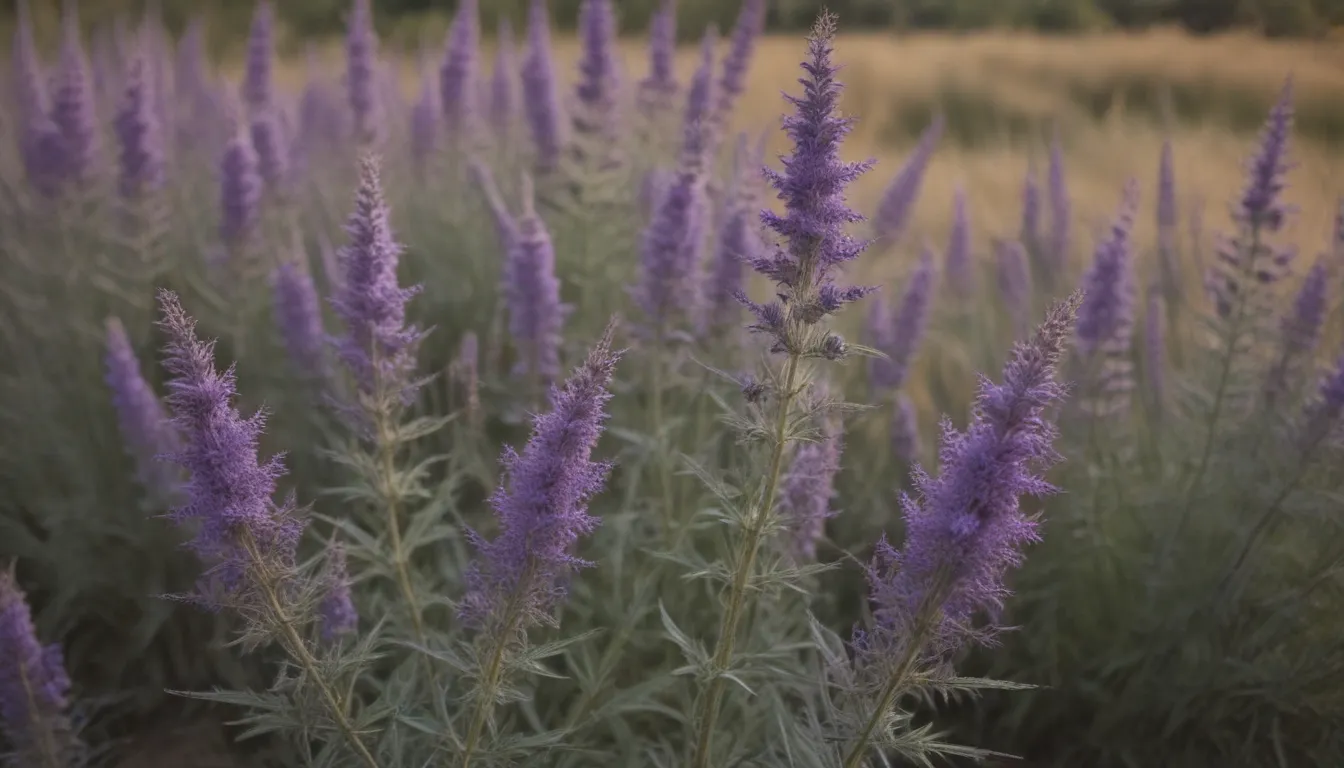

Are you looking for a low-maintenance, drought-tolerant plant to add to your garden? Look no further than Russian sage. This beautiful sub-shrub is often grown as a perennial and is known for its ability to thrive in dry conditions. In this in-depth guide, we will cover everything you need to know about growing and caring for Russian sage so that you can enjoy its long blooming period and striking foliage.
Getting to Know Russian Sage
Russian sage, previously classified as Perovskia atriplicifolia, was officially reclassified in 2004 as Salvia yangii. This plant is native to Asia, specifically the mountains of Tibet and Afghanistan. Russian sage produces panicles of small, bluish-lavender flowers throughout the summer and into fall. However, it’s not just the flowers that make this plant special. The silver stems and feathery leaves of Russian sage also add to its overall appeal. When fully grown, Russian sage can reach a height of four to five feet with a spread of three feet or greater.
Russian Sage Care Tips
Russian sage is a tough plant that requires minimal care. Here are some essential care tips to ensure your Russian sage thrives in your garden:
Light
Plant Russian sage in full sun for the best results and blooms. Shady conditions can cause the plant to become leggy and prone to collapse.
Soil
Russian sage thrives in dry, well-drained soil. Avoid planting it in dense, poorly drained conditions as it may develop root rot. This plant prefers alkaline soils of pH 7 and greater but can tolerate a range of soil pH levels.
Water
While new transplants may need regular watering, established Russian sage plants are very drought-tolerant. They prefer medium to dry soil and will do well in hot, dry areas. Avoid planting Russian sage in wet, poorly draining soil.
Temperature and Humidity
Russian sage is hardy in planting zones 5 through 9 and can survive in zones 3 and 4 with minimal protection during winter. In warmer regions, it behaves as a semi-woody shrub, while in colder zones, it acts as a perennial that dies back each winter.
Fertilizer
Russian sage thrives in average, well-drained soils and does not require much fertilizer. Avoid over-fertilizing, especially with nitrogen, as it can hinder plant growth.
Types of Russian Sage
There are several types of Russian sage available, each with its own unique characteristics. Some popular cultivars include:
- Perovskia ‘Little Spire’
- Perovskia ‘Blue Spire’
- Perovskia ‘Filagran’
- Perovskia ‘Longin’
- Perovskia ‘Blue Haze’
Pruning Russian Sage
Many gardeners choose to prune Russian sage annually to encourage bushier growth. Pruning can be done in the fall or early spring, depending on your preference. Cut back the stems to 8 to 12 inches to retain growth buds for the next season.
Propagating Russian Sage
Propagation of Russian sage can be done through basal cuttings or by dividing the plants every four to six years. You can also propagate Russian sage through natural layering, where stems touch the ground and sprout roots on their own.
Growing Russian Sage from Seed
While named cultivars may not produce true seeds, pure species plants can be grown from seeds. Sow the seeds in pots filled with a porous growing medium and keep them in a well-lit location. Germination typically takes one to four months.
Potting and Repotting Russian Sage
Russian sage can be grown in containers using a well-draining potting mix. Avoid rich potting mixes and repot the plant every couple of years. In cold-winter regions, move potted plants to a sheltered location during the winter.
Overwintering Russian Sage
In warmer regions, little winter preparation is needed. In colder zones, protect the plant crowns with mulch and remove it in spring when new growth begins. Monitor the plant closely during extremely cold winters.
Common Pests & Plant Diseases
Russian sage is generally resistant to common insects but may develop root rot in wet conditions. Ensure the plant is grown in well-drained soil to avoid this issue.
Ensuring Russian Sage Blooms
To promote robust blooming, ensure your Russian sage receives at least six hours of direct sunlight daily. Avoid excessive fertilizing, as it can hinder flower production. Young plants may take time to establish and bloom fully.
Addressing Common Problems
Sprawling stems are a common issue with Russian sage. Provide support or stake the plants to keep them upright. Avoid over-fertilizing and ensure the plant receives ample sunlight for optimal growth.
Russian sage is a versatile and resilient plant that can add beauty to any garden. By following these care tips and recommendations, you can enjoy the long-lasting blooms and striking foliage of Russian sage year after year. It’s a great choice for xeriscaping and will thrive in a variety of garden settings. Experiment with different cultivars and planting locations to see how Russian sage can enhance your outdoor space.
References:
– Texas Master Gardener
– Missouri Botanical Garden
– Wisconsin Horticulture Division of Extension
– Bird, Richard. The Propagation of Hardy Perennials. Batsford Publishing, 1994.
– University of Iowa
So, whether you’re a seasoned gardener looking to expand your plant collection or a beginner eager to try something new, consider adding Russian sage to your garden. Its low-maintenance nature and striking appearance make it a valuable addition to any landscape. Experiment with different planting techniques and care routines to find what works best for your Russian sage plants. With a little attention and care, you can enjoy the beauty of Russian sage in your garden for years to come.