What is a Node on a Plant?

Introduction
Plants are fascinating organisms with intricate structures that allow them to grow, thrive, and reproduce. One crucial component of a plant’s anatomy is the node. But what exactly is a node on a plant? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the world of plant nodes, their functions, and their significance in plant growth and development.
Understanding plant nodes is essential for gardeners, botanists, and anyone interested in the inner workings of the natural world. These small but mighty structures play a vital role in shaping the overall form and function of plants, from the tiniest herbs to the tallest trees. Let’s dive in and discover the secrets hidden within these remarkable plant features.
What is a Node on a Plant?
A node on a plant is a critical point along the stem where leaves, buds, and branches emerge. It’s essentially a junction or connection point that plays a crucial role in the plant’s structure and growth. Nodes are typically slightly swollen or thickened areas on the stem, and they’re where much of the plant’s important developmental activity occurs.
Key characteristics of plant nodes:
- They are the sites where leaves attach to the stem
- Axillary buds, which can develop into new branches or flowers, form at nodes
- Nodes contain specialized tissue that allows for new growth and branching
The space between two nodes on a plant stem is called an internode. The length of internodes can vary depending on the plant species and growing conditions, affecting the overall appearance and structure of the plant.
The Importance of Nodes in Plant Growth

Nodes are essential for several aspects of plant growth and development:
- Leaf Production: Leaves emerge from nodes, allowing the plant to capture sunlight for photosynthesis.
- Branching: New branches develop from axillary buds located at nodes.
- Hormone Regulation: Nodes play a role in the distribution of plant hormones, influencing growth patterns.
- Structural Support: They provide strength and stability to the plant’s overall structure.
Understanding the function of nodes can help gardeners and horticulturists make informed decisions about pruning, propagation, and plant care.
Types of Nodes
Not all nodes are created equal. There are several types of nodes found in plants:
- Leaf Nodes: The most common type, where leaves attach to the stem.
- Floral Nodes: Where flowers or inflorescences develop.
- Branching Nodes: Points where new branches or stems emerge.
- Root Nodes: Found in some plants, where adventitious roots can develop.
Each type of node serves a specific purpose in the plant’s life cycle and growth pattern.
The Anatomy of a Node
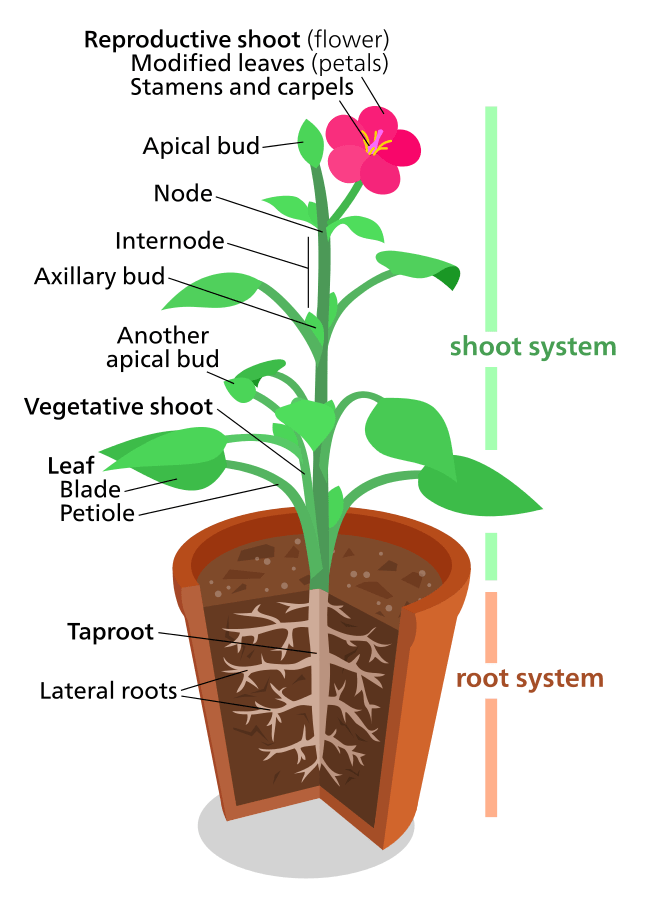
To truly understand what a node on a plant is, we need to examine its internal structure. A typical node consists of several key components:
- Vascular Tissue: Specialized cells that transport water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant.
- Meristematic Tissue: Cells capable of dividing and differentiating into various plant structures.
- Leaf Trace: Vascular connections that link the leaf to the main stem.
- Axillary Bud: A small, undeveloped bud that can grow into a new branch or flower.
This complex arrangement of tissues allows nodes to function as critical control points for plant growth and development.
The Role of Nodes in Plant Propagation
Nodes are particularly important in plant propagation, especially for methods like:
- Stem cuttings
- Layering
- Air layering
These techniques rely on the presence of nodes because they contain the necessary tissues and hormones for root development. When propagating plants, it’s crucial to include at least one node in the cutting to ensure successful rooting and new growth.
Nodes and Plant Hormones
Plant hormones, or phytohormones, play a significant role in the function of nodes. Some key hormones involved include:
| Hormone | Function at Nodes |
|---|---|
| Auxins | Promote cell elongation and suppress lateral bud growth |
| Cytokinins | Stimulate cell division and lateral bud growth |
| Gibberellins | Influence stem elongation and internode length |
The balance of these hormones at nodes determines the plant’s growth pattern, branching structure, and overall form.
Identifying Nodes on Different Plant Types

Nodes can appear differently depending on the plant species. Here’s how to identify nodes on various plant types:
- Herbaceous Plants: Nodes are often visible as slight swellings on the stem.
- Woody Plants: Nodes may be marked by leaf scars or bud scale scars on branches.
- Grasses: Nodes appear as distinct bands or joints along the stem.
- Vines: Nodes are often where tendrils or aerial roots emerge.
Learning to identify nodes on different plants can improve your gardening skills and botanical knowledge.
The Impact of Environmental Factors on Nodes
Environmental conditions can significantly affect node development and function:
- Light: Influences internode length and branching patterns
- Temperature: Affects the rate of node formation and development
- Nutrients: Proper nutrition is crucial for healthy node growth
- Water: Adequate hydration is necessary for node function and new growth
Understanding these factors can help you create optimal growing conditions for your plants.
Practical Applications of Node Knowledge
Knowing about nodes can be incredibly useful in various plant-related activities:
- Pruning: Proper pruning techniques often involve cutting just above or below nodes.
- Training Plants: Understanding node placement helps in shaping plants and controlling growth.
- Diagnosing Plant Problems: Issues like pests or diseases often manifest at nodes first.
- Hydroponics: Node spacing is crucial in many hydroponic setups.
Applying this knowledge can lead to healthier, more productive plants in both garden and agricultural settings.
Common Misconceptions About Plant Nodes
There are several misconceptions about plant nodes that are worth addressing:
- All bumps on stems are nodes: While nodes may appear as bumps, not all bumps on stems are nodes.
- Nodes are only important for branching: As we’ve seen, nodes serve many functions beyond just branching.
- All plants have easily visible nodes: In some plants, nodes can be quite subtle and difficult to spot.
Clearing up these misconceptions can lead to a better understanding of plant anatomy and growth patterns.
Conclusion
Nodes are truly remarkable structures that play a vital role in plant growth, development, and reproduction. From their role in leaf and branch formation to their importance in plant propagation, nodes are essential components of plant anatomy. By understanding what a node on a plant is and how it functions, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of the plant world.
Whether you’re a casual gardener, a botany enthusiast, or a professional horticulturist, knowledge about plant nodes can enhance your ability to care for and work with plants. As you observe the plants around you, take a moment to appreciate these small but mighty structures that contribute so much to the diverse and vibrant plant life on our planet.





