Comparing Heat Pumps and Furnaces: Finding the Best Heating Option for Your Home
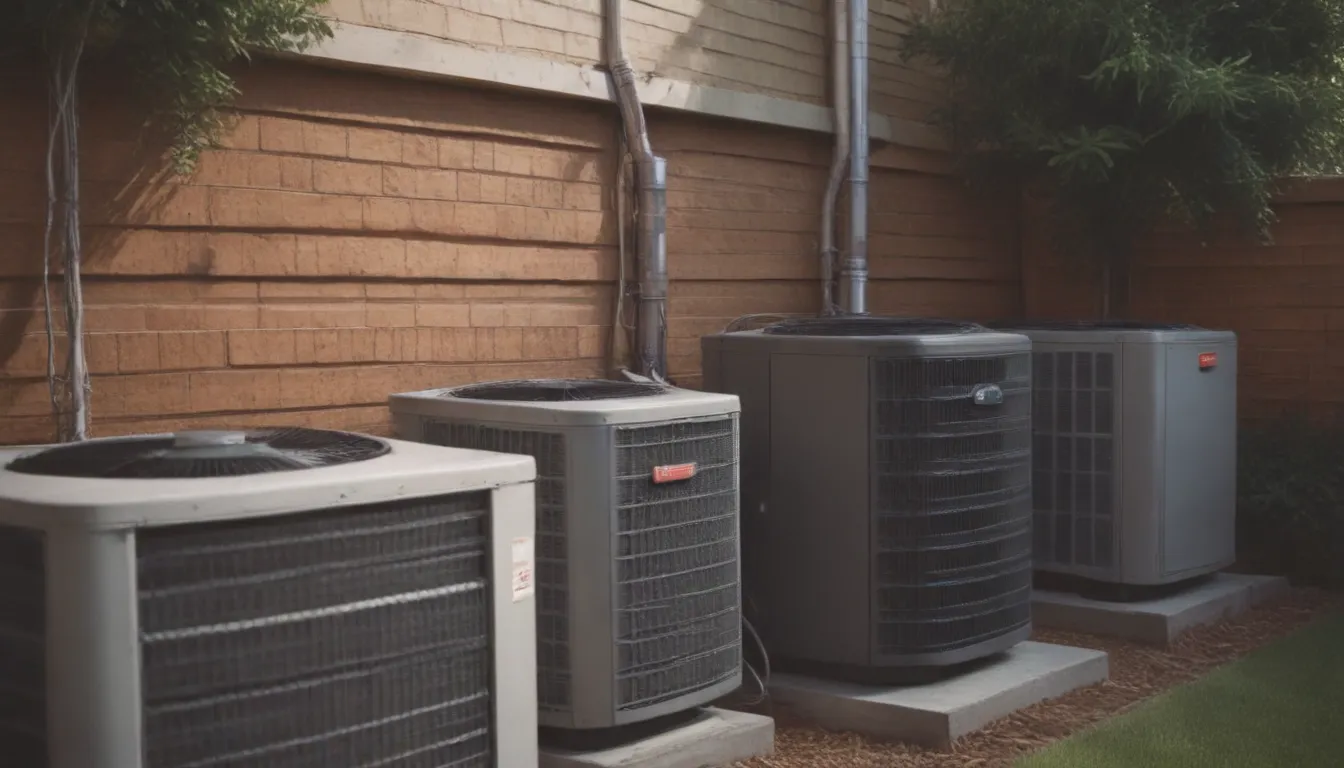

When it comes to keeping your home warm and comfortable, choosing the right heating appliance is crucial. Heat pumps and furnaces are two common HVAC options, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the key differences between heat pumps and furnaces, helping you make an informed decision on the best heating system for your home.
Understanding Heat Pumps
Let’s start by taking a closer look at heat pumps. Unlike furnaces that generate heat, heat pumps work by transferring heat from the air or the ground into your home. This process allows them to provide both heating and cooling functions, making them versatile HVAC appliances.
Key Features of Heat Pumps:
- Low operating cost: Heat pumps are known for their energy efficiency, which can lead to savings on your utility bills.
- High efficiency performance: They can reduce electricity usage significantly when compared to electric baseboard heaters and furnaces.
- Heating and cooling capabilities: Heat pumps can both warm your home in the winter and cool it in the summer.
- Space-saving design: They take up less space than traditional furnaces, making them a great option for homes with limited space.
However, it’s important to note that heat pumps may have some limitations, such as:
- High installation cost: The initial cost of installing a heat pump can be higher than that of a furnace.
- Noise: Heat pumps can be noisier than furnaces, especially when they turn on or off.
- Performance in cold climates: Heat pumps may struggle to operate efficiently in sub-freezing temperatures.
Exploring Furnaces
On the other hand, furnaces generate heat by burning oil, natural gas, propane, or using electric heating elements. They are particularly effective in colder climates where temperatures often drop below freezing.
Key Features of Furnaces:
- Relatively quiet operation: Furnaces are generally quieter than heat pumps.
- Efficient heat production in cold climates: They excel at providing warmth even in the coldest winter months.
- Long lifespan: With proper maintenance, furnaces can last over 20 years.
Despite their advantages, furnaces have some drawbacks, including:
- Higher operating cost: Furnaces can be less energy-efficient than heat pumps, leading to higher heating bills.
- Need for an air conditioner: Furnaces require a separate air conditioning unit to cool the home in the summer.
- Bulky size: They can take up a significant amount of space in your home, particularly in the basement.
Comparing Heat Pumps and Furnaces
Efficiency:
- Heat pumps: Known for their high efficiency and cost-saving benefits.
- Furnaces: While gas and oil furnaces are more efficient than electric ones, they come with potential risks associated with fuel combustion.
Climate:
- Heat pumps: Ideal for warmer climates where they can efficiently draw in heat from the air or ground.
- Furnaces: Better suited for colder climates, providing reliable heat even in sub-freezing temperatures.
Cost:
- Heat pumps: The operating cost is generally lower than that of furnaces.
- Furnaces: Initial purchase and installation costs are often more affordable than heat pumps.
Noise:
- Heat pumps: Can be noisier than furnaces, especially during startup and shutdown.
- Furnaces: Tend to operate more quietly than heat pumps.
Space:
- Heat pumps: Take up less indoor space, with the compressor located outside.
- Furnaces: Require indoor installation and can be bulky, occupying more floor space.
Lifespan:
- Heat pumps: Typically last around 15 years with proper maintenance.
- Furnaces: Have a longer lifespan of 15 to 20 years, with some models lasting up to 30 years.
Maintenance Tips for Heat Pumps and Furnaces
Both heat pumps and furnaces require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Here are some essential maintenance tips for each type of heating system:
Heat Pump Maintenance:
- Keep the compressor free of ice and snow during winter.
- Remove debris that blocks airflow around the unit.
- Clean the coils and replace the air filter regularly.
Furnace Maintenance:
- Replace the air filter every one to three months.
- Vacuum the ductwork annually.
- Clean the flame sensor to ensure efficient operation.
Choosing the Right Heating System for Your Home
In deciding between a heat pump and a furnace, consider the climate of your region, your budget, and your household’s heating needs. Here are some factors to keep in mind:
- Climate: Choose a furnace for cold climates and a heat pump for warmer regions.
- Efficiency: If energy savings are a priority, a heat pump may be the best option.
- Cost: Consider both the initial purchase price and long-term operating costs.
- Space: If space is limited, a heat pump’s compact design may be more suitable.
By weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each heating system, you can make an informed choice that meets your home’s heating requirements effectively.
In conclusion, the decision between a heat pump and a furnace ultimately depends on your specific needs and preferences. While heat pumps offer energy-efficient heating and cooling capabilities, furnaces excel in providing reliable warmth in cold climates. By understanding the differences between these two HVAC systems, you can select the best option for your home and enjoy year-round comfort and efficiency.
Remember, regular maintenance is key to prolonging the lifespan of your heating appliance and ensuring its optimal performance. Whether you opt for a heat pump or a furnace, prioritize scheduled maintenance to keep your HVAC system running smoothly for years to come.
For more information on heat pumps vs. furnaces, check out resources such as Heat Pump Systems. Energy.Gov and Bob Vila’s article on which heating system is best for your home. Making an informed decision about your heating appliance will not only keep you cozy but also help you save on energy costs in the long run.